Firearm

About twelve hundred years ago in China, some people figured out that certain chemicals mixed together (such as potassium nitrate, carbon, and sulphur) exploded when brought to spark, which became known as "black powder." After some experimentation, they discovered that a tube sealed off at one end could be used to focus said explosion to propel an object at high speeds. After a few centuries of refinement, they managed to take that mechanical principle and apply it as a weapon of warfare which changed the game: the arquebus. Comparatively cheap, easy to make, easy to learn to use, and capable of penetrating all but the heaviest armor, this marked a transition away from close quarters to ranged warfare.
In modern times, firearms are the staple weapons of any nation. Speculative fiction showcases weapons that doesn't even fire solid projectiles, like lasers.
From an engineering standpoint, firearms had a big difference from previous weapons in that they don't require the user's muscle power to work. Swords, maces, and axes are swung, spears are thrust, and bowstrings need to be drawn. Even a crossbow works by storing muscle power in the bow's tension until it's released. The energy required to accelerate a firearm's projectile comes from explosive propellants; all the user needs to do is to hold the weapon, aim and set off said explosive charge. The significance of this is illustrated in the American Proverb "God made man, Sam Colt (the inventor of the first practical revolver) made them equal": that having a reliable repeating gun means that your simple brute physical strength does not mean as much in a fight as it would in a bare knuckle brawl or a swordfight (either defensively or offensively).
The firearm's bigger bro is the Cannon and its cousin is the Rocket.
A Brief History of Firearms

1000s to 1200s: The Chinese realize they can make barbarians shit their pants by shooting hollowed arrows packed with powder and bamboo tubes filled with powder and pebbles at them. Bamboo gradually gives way to cast iron and bronze.
1300s: Various gunpowder weapons begin to proliferate westward along the Silk Road, aided by the Mongols. Crude versions of hand cannons, grenades, rockets, and flamethrowers all see use. Despite considerable psychological effect and good armor penetration, most of these weapons are only marginally more likely to kill the target than the user and had a range of only twenty or so meters. As such, their use is not widespread. For the most part, these weapons were used by skirmishers. The fact that they were mostly used by low class soldiers meant that the smiths making them were generally not the most skilled artisans which did little to improve quality even given the limitations of the day. Even so, the designs and methods of manufacture were gradually refined and improved by various early gunsmiths through trial and error.
1400s: Hand cannons see continued and expanded use. Bit by bit from the crude handgonnes of previous centuries, the first "true" firearms evolve with the gradual development of the matchlock, taking on the basic shape of lock, stock, trigger, and barrel (which is where we get the saying from). By clamping a lighted wick into a flashpan via a trigger, the shooter is able to aim and fire at the same time, making him markedly less likely to blow his own jimmies off. Despite advances, the matchlock was unwieldy, unreliable, and generally inferior to a good bowman. The issue of course is that only England (in Europe) HAD good bowmen; bowmen were the scum of the army everywhere else. This didn't stop some inventive commanders from seeing their potential, particularly with poorly trained conscript soldiers. Some forces made a go of it by carrying two or three guns at a time and just throwing the spent ones away like a really shitty Matrix movie. Note: while we use a "weeaboo" hyperlink up there, it's worth remembering that troops like cuirassiers and even pirates did the same thing, they just did not exist by the 1400's, having more then one gun was the only way to have any real rate of fire before breechloaders existed.
1500s: Guns continue to evolve with the invention of spring-loaded firing mechanisms. The wheel-lock spins a steel plate against sulfide rocks to produce sparks (think cigarette lighters), which ignites powder a flash pan. This was revolutionary, allowing soldiers to prime their weapon in a matter of seconds instead of fucking around with a lit wick, and allowed calvary to use guns for the first time while on horseback, giving rise to the cuirassiers. It also means that for the first time, guns weren't completely fucked in the rain, just mostly fucked. They also cost a lot to make and were still not completely reliable, so most people stuck with matchlocks. Powder formulas had improved considerably, including the development of the more powerful, stable, and moisture-resistant corned powder made by wetting raw gunpowder, forming it into cakes, crushing them, and sieving them for size. Japan was particularly notable in the history of firearms for their heavy transition from blades to guns after discovering the novelty of matchlock guns, more so that any country during that time. In fact, by the end of the 1500s, they had more trained arquebusiers in their armies and produced more matchlocks than any other country to date during that period.
A general note of terminology: 'arquebus' and 'musket' are both used to describe firearms from this time and they are often used interchangeably. But if you want to be really technical in this period an Arquebus is a regular two handed matchlock firearm while a musket is a larger heavier gun firing a large projectiles, sometimes up to an inch in diameter. Latter (about 1700 onward) musket would refer to any muzzleloading long barreled handheld firearm used for mainly shooting solid shots. This is not too much of a big deal and is nothing to get mad about, but it is worth noting.
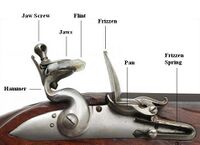
1600s The wheellock is refined into the simpler and more reliable flintlock, though it would take some time to supersede the matchlock. Muzzle loading is simplified with the creation of paper cartridges, essentially the pre-measured cake mix of murder. Some German dudes came up with the idea of cutting spirals into the barrel, which they called "rifling," to spin-stabilize the bullet so that they wouldn't have to walk up right next to their targets to hit them, but this required a barrel tighter than a nun's cunt, a hammer to ram the ball in, and grooved bullets made for the gun so it could fit the rifling of the gun like the cap to a soda bottle. To put all that into perspective: well trained musketeers could fire three to four shots a minute, while a rifleman could only manage one shot every minute.
1700s: The French invent the bayonet, allowing their troops to be choppy while they were shooty. This is the point where gun infantry tactics become the dominant (though still not only) form of fighting, when guns go from one a few common infantry weapons to the primary weapon used by most infantry. Formations of musketeers go from big square blocks to lines two or three ranks thick to put enough bullets in the enemy's ranks as quickly as possible.

1800s: Pretty much everything that makes up a modern firearm is invented here. Some fool came up with an explosive that would go off if you slam a hammer into it, which led to the first explosive primers. This basically involves putting explosives in ur explosives to explode your explosives. Cartridges that contain a primer, propellant, and slug, similar to modern-day bullets, are developed. By this time, wars were largely fought using firearms rather than melee weapons, though also by this time firearms were also melee weapons. in the early 1800 the bayonet charge was still an both accepted and useful tactic.
By the late 1800 inventors had finally gotten the technology to contain the force of the gun powder explosion with a tight seal and do so cheaply. Experiments that had been done earlier like the Puckle gun (1718), Ferguson rifle (1776), and even the bizarre 1780 Girandoni Air Rifle, which was an air gun with a 20 round magazine, all failed to create breech loading rifles cheaply. See, despite that it was well known that that slotting in bullets from the rear and using a mechanism to load it into the chamber is much simpler than spending about half a minute to ram it down a long barrel, the technology was just not there as without cheap steel (cheap is important for hand guns you are going to mass-produce), getting iron to contain the explosion with out deforming and leaking gas, thus weakening the shot, was a nightmare. The Industrial Revolution, among other things, gave birth to the concept of "breach-loading" and later "magazines" and simpler mechanized feeding systems like tubes, slides, cylinders, and bolt-actions. The likes of pump-action shotguns, bolt-action rifles, and lever-action rifles, and revolver and semi-automatic pistols, are developed and/or developed upon, giving a glimpse on how weapons in the future would function. Near the end of the decade, some French guys worked out that they could both improve firepower and keep their guns considerably cleaner by replacing black powder with nitrocellulose, the first of many "smokeless powders."
Just as important as the new designs that came about during this period were the new methods of production. People like Eli Whitney worked out devices such as milling machines, which allowed for the quick production of finely tuned parts which were so close in size that you could take one bit off one gun, stick it on another from the same line, and it would work just as fine. Breech loading and repeating firearms had existed for centuries beforehand, but were not cost effective to mass produce until the Industrial Revolution.

This is also the time where the first "automatic" guns are being invented and put into production. The word "automatic" is in quotes because these early machine guns were not self reciprocating; they did not load and fire themselves and were instead manually powered. The most famous (and successful) of these weapons is the Gatling gun, which saw limited action in the American Civil War, but became much more widely used the world over in subsequent wars. But while it was the most famous, the Gatling was not the only manual machine gun developed; dozens of different types were produced during the US Civil War alone on both sides, but because these guns tended to be mounted on cannon carriages, they were treated like cannons, not the close support weapon machines guns are, so it took some time for them to hit their stride.
1900-early 1930s: The heyday of guns because of the advent of WW1. The idea of bolt-action rifles are popularized, along with semi-automatic and fully-automatic weapons. Bolt-action rifles meant that riflemen no longer had to be confined to shooting one round at a time before needing to reload as they could now load individual clips that contained 5-10 rounds a piece. Machine guns are now becoming more and more popular in the battlefields, drastically changing the way infantry would maneuver the battlefield as a single MG emplacement can effectively cripple platoons with the right positioning. Submachine guns, the first automatic infantry weapon, are developed by the German Empire and issued to their stormtroopers, giving the rest of the world an idea of the wonders of a lightweight fully-automatic weapon that could easily be used by infantrymen, which was previously restricted to crew-served heavy machine guns.
On the subject of the nachine guns, if there was ever a weapon that represented this part of history it would be the heavy machine gun. to go back to an early quote "God made man, Sam Colt made them equal and John browning (designer of a large number of machine guns including the m2 .50 cal or 12.7mm) made them civilized. We talked about the hand powered machine guns above, and while good when used correctly, this weapons have their issues. In order to use most of them, you had to be standing up to turn the crank and sustained fire was tiring, but the hand cranked guns had one major advantage: the most successful of the hand-cranked guns, like the Gatling or Gardner, had multiple barrels meaning you can fire them with little or no need to stop to let the barrels cool down. At the dawn of the 20th century, this is what the early machine guns had to be compared to when European generals went window shopping. The solution was water-cooling, which allowed machine guns to fire for countless hours with little or no failures, but at the cost of weight rendering them truly static, though highly effective, weapons. If you could point to two developments that caused the First World War's trench warfare, you can point to water-cooled machine guns, and barbed wire.
late 1930s-1940s: At the start of World War II, all of the powers involved, France, England, Germany, and Russia, were armed with bolt action weapons. Over the course of the war, automatic and semi-automatic rifles started to become more common; however only the Americans completely phased out bolt-action rifles for standard infantry by the time of the war. Submachine guns are now becoming more popular with various armies around the world, making it the staple lightweight automatic weapon for infantry troops, totally re-defining urban combat due to the weapon's great effectiveness in close combat. Nazi Germany invents the Sturmgewehr 44, the first widely produced assault rifle (the Fedorov Avtomat was the first to be put into service, introduced in 1915, but production was limited due to costs). This weapon would later become the template for modern assault rifles used by the world over.

1950s-1990s: After World War II, the US Army performed a study and determined that it took 20,000 bullets to confirm one enemy casualty; most of those rounds would miss or be spent suppressing an enemy. With numbers like that, people now realized the power of a fully-automatic rifle since they allow you to fire more and more rounds and increase your chance of hitting as compared to a bolt action rifle. As such, assault rifles become more and more common with armed forces of the world and are extensively developed upon, largely, if not completely, phasing out the old bolt-action and semi-automatic rifles used back in WW2. Iconic assault rifles such as the AK-47, M14, and M16A1 are created and show the world the power of an automatic rifle through the the numerous wars going on during the 1960s-70s, such as the Communist wars in Korea and Vietnam, along with the Soviet occupation of Afghanistan, to name a few.
2000s: With the invention of more advanced materials such as plastics and carbon-fibre, along with numerous technological advancements of the modern world, firearms become more deadly than they were ever before. Fine-tuning how every aspect of how a firearm would work has allowed numerous countries to develop better and efficient ways on how to kill on a scale unseen since the Europeans developed the musket.
Many countries around the world are now looking for new ways to phase-out combustion-based firearms as a whole, and are looking for ways to make what were once sci-fi-only weapons, such as laser, plasma, and gauss guns, a reality. While met with some degree of success, nobody (as far as we know, anyway) has found a way yet for these weapons to be man-portable that a single soldier could carry these into combat or be affordable to an extent that it would be more feasible to make these instead of the traditional slugthrowers. There is also the problem that if you get a projectile going fast enough, it will just over-penetrate and go though a target, doing little actual damage as compared to our modern bullets that hit, create a temporary cavity the size of a dinner plate, then tumble going though the target sideways. So even if such projects were successful, there is a strong point to be made that, as least as far as infantry weapons are concerned, chemical slug throwers will remain both cost effective and lethal enough that such projects are dead ends.
Types of firearms
Having been around for well over 1500 years there have been many types of firearms over the course of time. Humans are, if anything, very inventive when it comes to coming up with new and interesting ways to kill each other. A rough list are:
- Handgun - Also called "pistols", handguns are small-sized firearms that can be comfortably fired in one hand. Akin to the dagger; handguns are mainly used for close defense and as a sidearm. Modern pistol calibers are commonly between 9 and 11mm.
- Machine pistol - A machine pistol is a pistol that can fire on full auto. While they're commonly thrown into that category; MPs are not submachine guns due to their size and use.
- Shotgun - Shotguns are smoothbore weapons, designed to fire either shot (multiple steel pellets) or slugs (a single, heavy projectile), although modern times have included other types of ammunition. The ability to fire multiple types of ammunition without modification is one of the main advantages to using a shotgun, converting an anti-infantry weapon into a door-breaching tool, a mini-flamethrower, or a non-lethal weapon. The vast majority of shotguns are pump-action or breech-loading, though military shotguns can come in semi-automatic, or very rarely, fully-automatic configurations.
- Rifle - Rifles were originally shoulder-fired weapons that had their barrels "rifled" to increase precision, which was an act by putting spiral grooves into the barrel to give the round more momentum. However, because most modern firearms now use rifling to improve ballistics; a shoulder-fired long weapon is usually classed as a rifle.
- Assault Rifle - Assault rifles are a term given to any rifle that can be fired on full-auto and shoot intermediate-caliber rounds, typically in the 5mm range (or a shortened 7mm round if you're from the Eastern bloc).
- Battle Rifle - Basically a bigger assault rifle; battle Rifles are bigger automatic rifles designed to fire high-caliber rounds, typically in the 7mm range.
- Carbine - Carbines are rifles with their barrels made shorter and the overall design is usually made more compact in comparison. These are typically given to units who need to, or only engage the enemy at close combat, like commandos, assault teams, or other specialist units, or given to units who are not expected to fight on the front but need a compact but decent weapon to defend themselves if the need arises, like pilots or vehicle crews.
- Micro Assault Rifle - Even smaller than carbines; these are ultracompact rifles designed when someone needs a highly portable but powerful weapon. A MAR is basically a PDW that shoots rifle rounds.
- Sniper Rifle - A sniper rifle is a special precision rifle, specifically designed to engage targets at extreme range with lethal efficiency. Many sniper rifles use standard 7mm rounds, but high-performance rifles will use magnum (extra-power) rounds or 12mm rounds for extra range and stopping power.
- Designated Marksman Rifle - A sort of compromise between battle rifles and sniper rifles, DMRs are precision weapons meant to be used by frontline infantry to accurately engage distant targets. This is in contrast to snipers, who are usually well away from the front and pick off targets from a relatively safer and concealed position.
- Recoiless Rifle - Not a conventional rifle in the sense; a recoiless rifle is an anti-tank weapon. This weapon uses a rifled bore to aid in the momentum of its projectile, allowing it to snipe armored vehicles (and unlucky infantry) with lethal precision.
- Submachine nun - An SMG is a fully automatic weapon that fires pistol cartridges, instead of the larger rifle cartridges. One of the first true fully automatic infantry weapons outside of the machine gun; the weapon fulfills a similar role of the carbine in that its a weapon made for infiltrators and assault units, as its compact size and power makes it a close-rang powerhouse.
- Personal Defense Weapon - A PDW is a bit of a mix of a carbine and an SMG, firing specialized cartridges with rifle-like characteristics (usually in the 4-5mm range, shorter than a rifle cartridge but longer than a pistol cartridge) at the cost of additional weight. Its original role is as its name implies; a personal defense weapon for non frontline infantry, like artillery spotters, scouts, vehicle crews...etc. Back then, PDWs weren't necessarily automatic; a pistol with a longer barrel and stock could be classified as a PDW (This was done with the German C96 and Luger P07). These days, PDWs are commonly lumped into the same category as SMGs, as they now fulfill similar roles.
- Machine Gun - A machine gun is an large automatic weapon, typically fed from a magazine or a belt and meant to either be portable or fired from an emplacement (like a bipod or tripod). The main difference between MGs and the rest of the automatic weapon family is that an MG is a gun meant to be fired continuously as a support weapon; meaning that the machine gunner stays back to continually shoot at the enemy to keep them down (and occasionally kill those stupid enough to not get the message), while the rest of the squad advances. Machine guns are typically heavy, not only because of the volume of ammo they carry; but their parts are made of heavier materials so that the gun can withstand the punishing amounts of bullets it puts downrange (firing hundreds of rounds without pause can cause guns to overheat and malfunction, even catch fire or explode in the worst of scenarios.)
- Light Machine Gun - an LMG is a man-portable MG that fires the same intermediate rounds as assault rifles. They are intended to be almost as portable as a rifle and allow machine gunners to provide suppressing fire at the squad level. Some LMGs are usually magazine-fed rifles with heavier barrels and modified bolts, or else scaled-down MMGs.
- Medium Machine Gun - an MMG is a man-portable MG that fires the same full-power rounds as battle rifles. These tend to push the limit of what's practical for a man-portable weapon, and when deployed are usually fired from a stationary position either on a bipod or tripod due to the recoil they generate.
- Heavy Machine Gun - HMGs fire large caliber rounds (like the famous .50 cal). Unlike the other two; HMGs are exclusively meant to be fired from emplacements like a tripod due to their large size and weight, which makes them impossible to fire on the move, unlike the light and medium machine guns. HMGs are powerful enough to penetrate light armor, making them a formidable weapon.
- Rotary Machine Gun - Originally known as the "Gatling gun", man's first known attempt to have enough dakka; a rotary machine gun is an automatic weapon that uses revolving barrels that interchange every time the gun fires off a round. The kicker to this is that it allows the gun to shoot with little threat of the barrels wearing out as they interchange between shots; giving them a small window to cool off before firing again. The end result is a gun capable of firing over 3,000 rounds per minute without fail, or in a smaller scope; 50 rounds per second. Modern rotary guns are electrically powered to allow them to reach such insane speeds, and are given ammo drums that contain thousands of rounds to be able to sustain that amount of bullets being fired; so they're confined to static emplacements and vehicles (unlike what the media constantly portrays; these things are not even close to being man-portable without assistance from powered armor.)
- Chain gun - A chain gun is a machine gun that is fed using an electric motor. Instead of relying on the gasses from the bullet to work the action to cycle a new round; a machine automatically ejects and loads a new round in after firing a shot. Chain guns have the benefit of never jamming due to feeding failures, as even if the round is not discharged; the machine pops it out and loads a new one regardless. However, it is also not man-portable as it requires an electric motor to function, so it is only found on fixed emplacements or vehicles.
- Revolver: A revolving gun is any weapon that uses a revolving cylinder to chamber new rounds after every shot. While its commonly now relegated to pistols (a revolver typically meant a revolver pistol these days), the style is still used for shotguns (like the Armsel Striker) and grenade launchers (like the MM1-Hawk). Revolvers are still in use for two reasons: they jam less than semi-auto pistols, and they tend to be the only weapon that can handle magnum rounds.
- Multi-barreled: In the olden days, people wanted shootier guns, but things like magazines and self-loading weapons were still an alien idea during its time. So as an alternative; people took a breach/muzzle-loaded firearm, slapped one or more barrels onto it, and reworked the trigger so they can fire more shots before needing to reload. This resulted is some particularly wacky times for guns. To this day, the only multi-barrel weapon still commonly used is the double-barreled hunting shotgun.
Actions
"Action" refers to how ammunition is loaded into the weapon.
- Single-shot: The first and oldest of all; a single-shot weapon is when users manually load rounds into the chamber. This can be anything from loading a new round, cocking the weapon every shot, or pumping the action.
- Muzzle-loaded: The earliest form of how weapons were loaded; these meant you had to load a new round directly into the muzzle, which is where the bullets come out. In its earliest form; muzzle-loaded guns were complicated to arm; you had to fuck around with a wad, powder, and slug. In the heat of battle, you had to ram these down the barrel of your gun in correct order, light the wick, then aim before the gun goes off.
- Breach-loaded; An upgrade over muzzle-loading and developed shortly after cartridges were invented; breach loaders are where the bottom of the barrel can be unhinged so that you can load a new round into it. It is still a popular setup for multi-barreled shotguns.
- Bolt-action: This type of action is where you pull the charging handle of a weapon, every time you shoot so that the mechanism would chamber a new round. These were pretty popular in WW1 and continues to be used today for precision rifles.
- Lever-action: The cool kid of the single-action club; lever-action weapons are those where you have to use a lever to chamber a new round, which was usually mounted near the trigger. This type was made popular by Winchester during the frontier age of the Wild West and even more by Arnold Schwarzenegger when he used a lever-action rifle during Terminator 2.
- Pump-action: A pump action is where you had to pull the "pump" of the weapon to cycle a new round. This is the most common action used by shotguns.
- Semi-automatic: A semi-automatic weapon is any weapon that can fire after every trigger pull, with the user only needing to work the action after reloading a completely empty gun. Unlike single-shot weapons, it uses gasses expelled by the cartridge or recoil to power a mechanism that automatically chambers a new round after each shot. Most handguns and many rifles are semi-automatic.
- Fully-automatic: A fully-automatic weapon is any weapon that can fire automatically, so long as the trigger is depressed, rather than pulled each time like how semi-autos work. Automatic weapons tend to be banned for civilian use and are only available to military.
Relations here
Most fantasy writers tend to exclude firearms. There are a variety of reasons for this, such as:
- Most fantasy comes from Tolkien, who, being a naturalist who largely despised industrialization, did not put guns in Middle-earth, although gunpowder does exist, used by the wizards (Gandalf's Fireworks and Saruman's Fires of Orthanc) and by the orcs.
- Most fantasy (whether copy-catting Tolkien or not) is based on medieval Europe. Depending on your definition of "medieval," Europe did technically have firearms towards the very end (crude and unreliable ones, but firearms nonetheless), but most authors base their fantasy on earlier medieval Europe.
- As in real life, firearms mean that vulgar, dirty, peasant conscripts can take down the author's Mary Sue noblemen knights that trained so hard in the arts of swordsmanship and melee combat, though if the writer had any historical knowledge they would know that armor can be made "Proof" against bullets, which is partly what spurred the development of full-body plate mail to begin with.
All that being said, most fantasy authors are much more open to cannons, which became viable on the battlefield long before smaller firearms anyway.
Generally speaking, if a world has both the "stock" fantasy races and guns, there will a strict hierarchy of who uses them, from most to least likely:
- Dwarves: They almost always have the best, most plentiful guns. If only one race gets firearms, it's likely going to be them.
- Gnomes: As tinkerers, they're frequently on a different tech level from everyone else, including firearms.
- Humans: Unlike the other races, which are usually an all-or-nothing deal, different human nations have different likelihoods of having guns. Italian and east Asian analogues, as well as the "industrious" or "scientific" nations, are much more likely to have them. Your barbarians, guys keen on knights and chivalry, and the more conservative less so.
- Orcs: Orcs would probably love guns if they could actually build some. However, they're usually either incapable of building things or have a hard time organizing themselves to the point that large-scale firearm and powder production is possible. Even so, they could still obtain them them by other means such as fighting as mercenaries for guns and stealing them off the corpses of the fallen and similar. They are higher on the list if they are more like Tolkienian orcs, which can be fairly well organized and "delight in explosions" enough to manufacture their own gunpowder, if only for simple bombs.
- Elves: Being arrogant pricks, they see guns as crude, inaccurate, foul-smelling contraptions that are no substitute for a bow. However, they'll still use them when necessary, even if they don't like it. That said, elves also had a good reason to not use them, namely most firearms in a fantasy settling are arquebus-type single-shot smoothbore weapons, which are outranged by longbows. Longbows are even decent against most kinds of armor (ask the French). The main advantage of firearms, even early ones, is ease of use and armor penetration though armor could be made that could stop a early handgun. The main problem with longbows is that it takes years to learn, which is not a problem for long-lived elves. Between a smoothbore handgun and a longbow, the bow is simply a better choice to an elf.
- Wood Elves and other Fey/Nature types: They'd rather die than use a firearm, even if the rest of the world has moved onto biplanes, bolt-action rifles, shell-firing cannons, and tanks. If this happens, this means they either have powerful magic (so the actual weapons used are unimportant), they are really really good shots with a bow, or they're about to die out.
Of course, sci-fi writers almost exclusively use firearms, seeing as how it's THE FUUUUUUTTTTTUUUUURRRREEEE. The exceptions are Warhammer 40,000 and Dune: although guns are the main combat implement in 40K, close combat is still alive and well, and most armies have at least one elite, close-combat unit wielding weapons that are distinctly not firearms; in Dune, guns are pretty much dead as a weapon of war, as personal-scale force fields stop fast-moving matter (like bullets) from crossing them, but slower matter (like swung knives) can pass through, and if a lasgun blast touches the field, at least one end of the equation comes out "BOOM!!!". Most sci-fi universes do have close combat weapons on the scale we see in modern warfare, though, like in Mass Effect, where, as the Reaper forces (who are basically Necrons and Tyranids combined) invade the galaxy, people begin developing their Omnitools to snap-produce a white-hot blade of hard metal above the wearer's hand... And then there's the Krogan, who are too bloodthirsty and too large to properly take cover, so they headbutt things instead of using guns.
Rules
Most fantasy RPGs deal with firearms the way they deal with lots of things that threaten their Medieval Stasis: terror, suspicion, and shitty rules. If you have the option of using a firearm in most games, it probably has one shot that's weaker than a bow, then takes an entire encounter to reload, and is illegal everywhere in-setting in case you didn't get the hint.
BECMI Dungeons & Dragons doesn't have rules for firearms, but there were one or two adventure modules that incorporated a crash-landed spaceship, with weapons the players could loot. They were treated as magic wands and staves. A few issues of Dragon magazine offered rules for early cannons and hand cannons.
Advanced Dungeons & Dragons mentions guns in a tucked-away subsection on importing TSR's cowboys & indians game Boot Hill to AD&D (DMG, pg113). Revolver pistols and gatling guns would do as much damage as a longsword; shotguns as much damage as a two-handed claymore, a (thrown) stick of dynamite does 4x the damage of a short sword. The rules insist "...when gunpowder is brought into the fantasy world it becomes inert junk, ergo, no clever alchemist can duplicate it." To reinforce this concept, the Manual of the Planes included rules for factors of prime material planes, one of which determined if complex (read: setting destroying) chemical compositions like black powder would even work in said plane. If you have any knowledge of chemistry, you may cry now. Notably, Greyhawk had a god of firearms, and his paladins were basically Wild West sheriffs.
Advanced Dungeons & Dragons Second Edition included the arquebus in the Players Handbook, where they were depicted as slow, powerful and expensive (500 Gp!). They were also potentially dangerous to the user as the result of a bad roll. It was painfully stressed that the inclusion of firearms in the campaign was the call of the DM. Firearms were a bit more common in the Spelljammer setting. Moving away from the classic fantasy background, there was the historical campaign sourcebook A Mighty Fortress that introduced rules for firearms of the 16th and 17th centuries and the Masque of the Red Death setting for Ravenloft pushed everything into a gothic horror version of the 1890's.
D&D third edition has a section on advanced technology (DMG, pp162-164) for Renaissance-era, 20th century, and futuristic weapons. The weapons are more powerful than what can be found among ranged weapons in the Player's Handbook, but also heavier and more expensive. You're better off with magic crossbows.
Pathfinder seems to do early firearms right: they have shorter range than bows without magical items, take longer to reload, have a chance to break or explode on a misfire, and use up more expensive ammunition, but they hit harder, have a terrifying 4x crit modifier, and use touch AC in the first range increment, effectively ignoring armor when fired close up. Probably the only things restricting their use so heavily are the stiff feat tax needed to make use of them and the fact that there's really only one major gun factory in the land, the Gunworks of the small nation of Alkenstar, and they keep most of their guns to themselves. A specialized class, the gunslinger, is centered around the use of firearms.
Dragonmech has guns, sort of kinda, as well. Only instead of using gunpowder they use steam to propel the bullet like an air gun. they can only be fired once every other round as the pressure needs to build up. There Treated a bit like cross bows that do more damage and can shoot a little further.
Dungeons & Dragons 5th Edition includes a section on firearms in the Dungeon Master's Guide. They hark back to 2nd edition in terms of stats, fitting the general tone of the game, but aren't quite as punishing for a player to learn to use and make. And with the increased emphasis on houseruling and homebrewing, modding the crossbow expert feat to work for them seems a simple leap of logic. The "race builder" guide in the back even suggests changing around the dwarf weapon proficiencies to include them! Furthermore, if you want to get your Expedition to the Barrier Peaks on, it includes some futuristic guns as well, like lasers and disintegrators.
| Medieval Weaponry | |
|---|---|
| Melee Weapons: |
Battleaxe - Dagger - Lance - Mace - Club Pole-arm - Spear - Sword - Warhammer |
| Ranged Weapons: |
Blowgun - Bows and Arrows - Cannon Crossbow - Firearm - Rocket - Shuriken - Sling - Incendiary Weapons - Artillery |
| Armor: | Armor - Fantasy Armor - Helmet - Pauldron - Shield |